Universe Unfold

The Evolution of Theories
This post was written by Aryaka Choudhary, Abhay Gupta and Khushi Baghel for the first SpaceWalk by STAC IIT Mandi.
SpaceWalks is a series of talks where speakers will present on various topics in the fields of Space Technology and Astronomy.
Think of the biggest question that humanity has ever asked, what comes to your mind..?
What is meaning of life or Why are we all here or perhaps even how did all of this start? How did the universe begin?
Most of the cultures around the world have some sort of story to explain the origin of universe which usually involve creator of some kind for example according to our Hindu Mythology the universe was created by Lord Brahma, who made the universe out of himself.
Let us see how scientists approach this curiosity

THE PULSATING THEORY
This theory was proposed by Richard Tolman around the 1930s. He was a mathematician at the California Institute of technology. Pulsating theory is also called an oscillating theory or cyclic universe theory. This theory states that the universe goes through regular expansion and destruction. The expansion phase is called as Big Bang and the contraction phase is called Big Crunch. The expansion of the universe occurs due to the initial impulse of the big bang and will stop when gravity overcomes the impulse and then the contraction phase will begin called the big crunch. In 1929, Edwin Hubble proved that currently, the universe is expanding. So, Tolman proposed that currently, the expansion phase is going on. The theory also postulates that the universe does not have a specific beginning or an end, it is built and destroyed alternately.
This is not an accepted theory but explains some shortcomings of the other theories like the thermal state problem. So, the contraction of whole matter and energy in the universe into a singularity produces a huge amount of energy which is sufficient to initialize the process of the big bang.
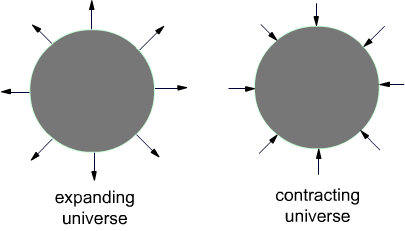
The Cyclic expansion and contraction of the universe
The Shortcoming of Pulsating Theory
This theory contradicts the second law of thermodynamics, ie entropy of the universe can never decrease. As in this theory, it is stated that the whole universe contracts to form a singularity resulting in a decrease in entropy
THE STEADY-STATE THEORY
“Things are the way they are because they were the way they were.” >
~SIR FRED HOYLE
Have you ever encountered a movie that changed your life? 3 Idiots or ZNMD? This is possible, but what if I say a movie that changed the theory on the universe’s formation? Yes, dead of night, the movie that had no beginning and no end, you could enter anywhere. This movie paved a path for Hermann Bondi, Thomas Gold, and Fred Hoyle to come up with the Steady State model of the universe in the 1940s, a cosmological belief that the universe looks the same from every place at all times.
The theory stated that although the universe was expanding it always remained balanced. The density of the universe was decreasing as the universe was expanding continuously and in order to balance the decrease in density of matter, Hoyle stated that new matter is continuously created. The new galaxies and clusters of galaxies are constantly being formed at a rate that compensates exactly for dilution in the density of matter caused by the expansion of the universe.
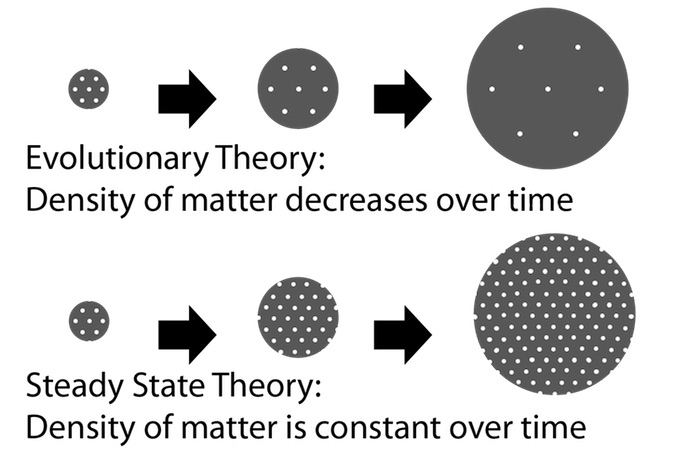
Credit: NASA’s Cosmic Times
The steady-state model of the universe is based on four assumptions together called the Perfect Cosmological Principle
- The first assumption was that physical laws are universal.
- On a large scale, the universe is homogenous.
- It was assumed that the universe is isotropic.
- In the universe, nothing changes with respect to time.
The Shortcomings of Steady-State Theory
The discovery of quasars told heavily against the steady-state theory. A quasar is an extremely luminous galactic nucleus. Quasars had large redshifts, which indicates that they are far away. Through luminosity and distance, we inferred that a quasar might be brighter than a whole galaxy.
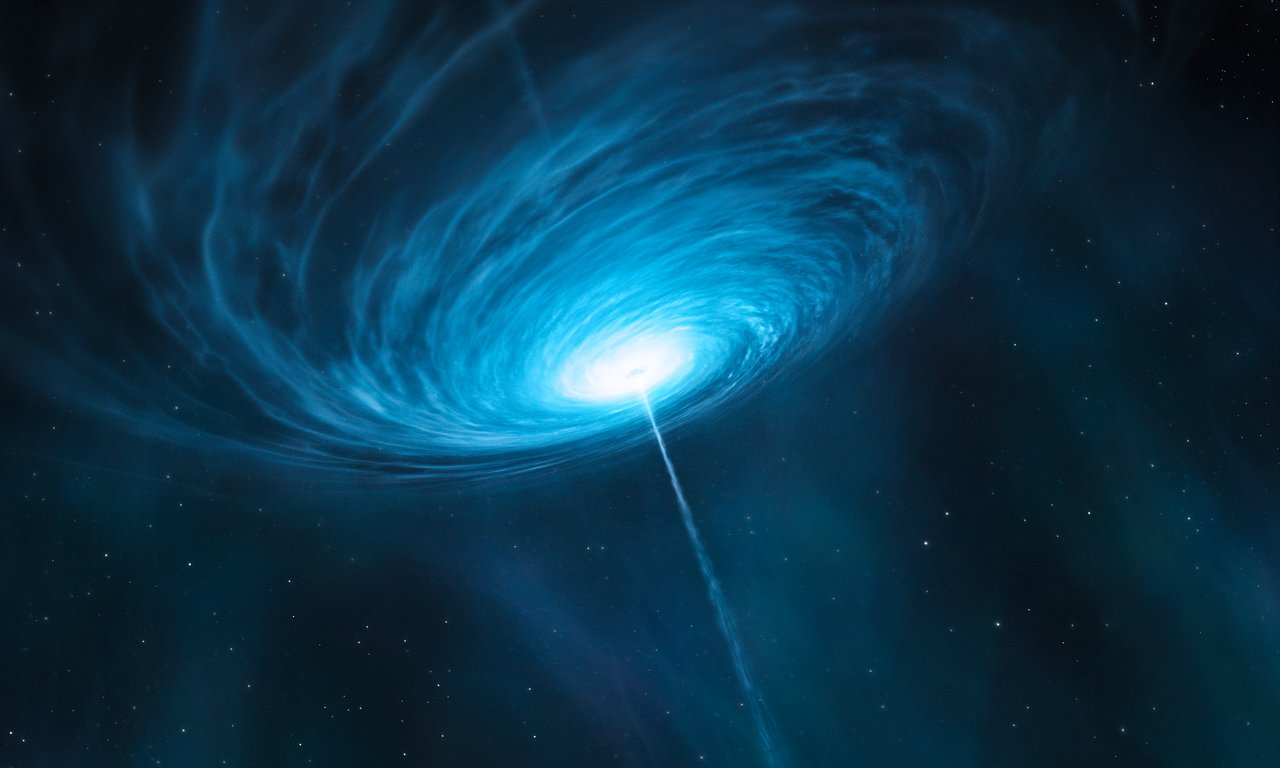

Impression of the quasar 3C 279 for an artist.(Credits: ESO/M. Kornmesser) A quasar is an extremely luminous galactic nucleus.
Rationally, there was no space for such objects in the steady-state universe, where contents of any region are nearly similar in the universe. This discovery made people rethink the steady-state model of the universe as the universe was evolving.
Later, the steady-state model wasn’t able to account for the Cosmic Background Radiation. To justify the cosmic background radiation, it was stated that these radiations were the light from ancient stars which was absorbed and emitted in all directions. But the radiations found could not have come from small multiple sources.This gave a deaf blow to the steady-state theory.
The Quasi-Steady-State Model
The Quasi-steady-state cosmology (QSS) started emerging in 1990s mainly by Sir Fred Hoyle, Geoffrey Burbidge, and Jayant V. Narlikar as a new avatar of the steady-state ideas that explained auxiliary features which were not included in the initial proposal.The new model suggested that small pockets of creation occur over time within the universe,referred to as mini-creation events,minibangs, or little bangs.Later, it was observed that the universe is accelerating, further modifications were made in the model.Wright and other mainstream cosmologists who reviewed the QSS have pointed out new flaws and discrepancies with observations left unexplained by supporters.
THE BIG BANG THEORY
“God created two acts of folly. First, He created the Universe in the Big Bang. Second, He was negligent enough to leave behind evidence for this act, in the form of microwave radiation.” >
~PAUL ERDOS, 1913 TO 1996
One of the most widely accepted ideas on the origins of the universe. Georges Lemaître proposed it for the first time in the 1920s. It states that, “the universe began as an expansion from a single point of infinite energy density.” Why is it so well-liked? What comes after the Big Bang? What are some of its flaws? Will see answers to these questions one by one. There were two main Eras after the Big Bang: The Radiation Era and The Matter Era.
Radiation Era (10^-42th sec – 300,000 years)
The Universe was dominated by the impact of radiations during this Era. It has major six epochs.
- Planck Epoch: It begins at 10^-42th second after the bang. Only energy and the Superforce (Gravity, Strong Nuclear, Weak Nuclear, Electromagnetic) exist at this time. The entire cosmos was 10^-20th the width of a proton, or Planck’s length.
- Grand Unified Epoch: Gravity was separated from the Electronuclear forces.
- Electroweak Epoch: The temperature had fallen enough that the strong nuclear force split from the electroweak forces, but it was still high enough that the electromagnetic and weak nuclear forces remained combined.
- Quark Epoch: All fundamental forces had split off and quarks were formed.
- Hadron Epoch: Quarks combined to form hadrons i.e., Protons and Neutrons.
- Lepton and Nuclear Epoch: At the very 1st sec after the bang first electron was created.
Matter Era (300,000 years onwards)
It has major three epochs.
- Atomic Epoch: At the age of 300,000 years first atom of universe was created.
- Galactic Epoch: Hydrogen and Helium combined together to form gas clouds, giving rise to the universe’s first galaxies.
- Stellar Epoch: Formation of Stars and Planets inside the galaxies.
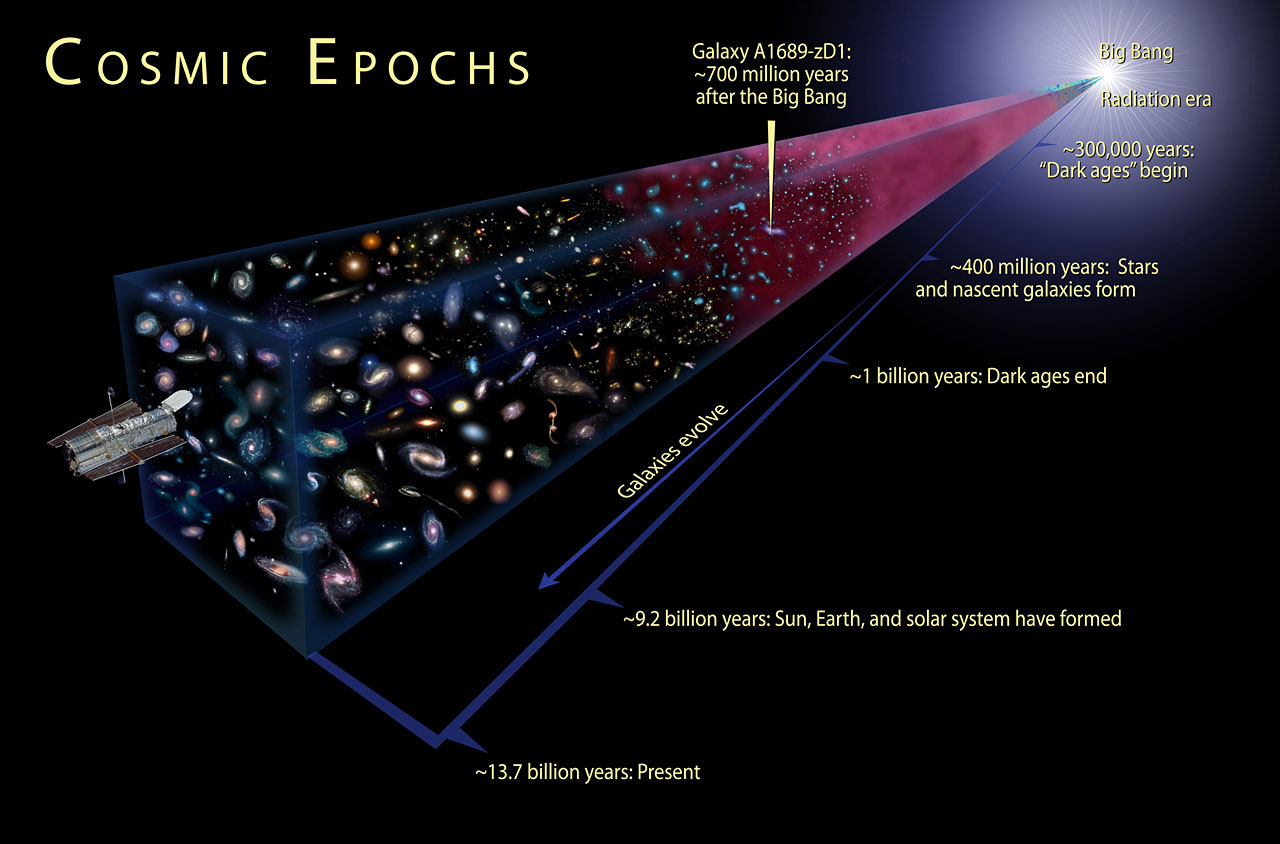
Credit: NASA, ESA, and A. Feild (STScI)
Is the Big Bang real?
- Universe is expanding: The confirmation of “Redshifts” led to the conclusion that the universe is expanding. When light from galaxies reaches us, it is stretched and pushed towards the red part of the spectrum, making them seem red to us as they move apart.
- Gas clouds seen by modern telescopes: When seen using modern telescopes, distant views reveal clouds of gas that have not yet evolved into stars and galaxies.
The Shortcomings of the Big Bang Theory
- Rapid expansion during the inflationary period: During the inflationary period (10-36th sec -10-32th sec), the universe experienced rapid exponential growth in a relatively short amount of time, violating the rule that nothing can travel faster than the speed of light.
Asking what happened before the Big Bang is pointless, according to the no-boundary hypothesis, much like asking what lies south of the South Pole. Because there is no concept of time to fall back on. Only within the cosmos does the idea of time exist.
 Never miss a story from us, subscribe to our newsletter
Never miss a story from us, subscribe to our newsletter